Seamless Sponsorship Revenue Recognition. Integrating Salesforce, NetSuite, business management and engagement marketing software for Professional Sports Organizations
Part I — Business & Integration Overview
1. Executive Summary
Modern professional sports franchises juggle complex sponsorship contracts that span multiple seasons, channels, and deliverables. When sales data lives in engagement marketing software or Salesforce while financial data lives in NetSuite, manual rekeying and spreadsheet work slow down monthend close and create risk under ASC 606.
This white paper explains a proven fivelayer integration pattern that:
Automates the transfer of Sponsorship and Premium/Suite contract data from engagement marketing software into Salesforce for near realtime sales visibility.
Posts the same contracts and related billings to NetSuite, where Advanced Revenue Management (ARM) recognizes revenue accurately and automatically.
Delivers auditready compliance, faster close cycles, and endtoend transparency, without exposing proprietary configuration details.
The guidance is written for CTOs, Directors of Business Systems, and enterprise architects within professional sports teams and similar organizations.
2 . Industry Context & Problem Statement
Fragmented Systems. Sponsorship operations typically run on the business management and engagement marketing software platform and a mainstream CRM, while finance relies on an ERP. Information silos force staff to reconcile data manually, delaying insights and inviting errors.
ASC 606 Complexity. Multi-element obligations (signage, digital assets, hospitality) require fairvalue allocation and timephased recognition. Spreadsheets struggle to scale.
Visibility Gaps. Sales and finance lack a single version of the truth, hampering forecasting and partner communication.
Operational Overhead. Manual journal entries and duplicate data entry extend the close process and consume resources.
Organizations need an integrated solution that eliminates redundancy, enforces compliance, and provides near realtime insights across departments.
3. Solution Overview
The integration is designed around a hubandspoke concept in which Workato acts as the central nervous system connecting the engagement marketing platform, Salesforce, and NetSuite. Each application continues to own its domain, the engagement marketing platform for sponsorship assets, Salesforce for relationship management and billing, and NetSuite for finance, while Workato ensures data flows are timely, validated, and traceable.
From a business perspective, this architecture gives every stakeholder the information they need in the system they already use: sales executives see contract status in Salesforce moments after a deal is signed; finance trusts that every performance obligation is already queued for revenue recognition in NetSuite; partnership operations can confirm asset delivery in engagement marketing software without circulating spreadsheets. The result is one fluid lifecycle from contract negotiation to cashinbank and revenue recognized.
Figure 1 – Highlevel architecture; each arrow represents a Workato recipe with validation, mapping, and error handling.
4. Integration Architecture
The architecture follows a layered pattern that separates triggers, transformation, orchestration, and persistence. This separation keeps the solution maintainable and lets each component evolve independently, for example, switching from REST to GraphQL endpoints, or adding new downstream systems.
Key Moving Parts
EventDriven Triggers in Salesforce fire when a new Deal or Invoice is created.
Workato Recipes transform payloads, apply validation rules, and call the engagement softare APIs or Redshift queries for supplemental data.
NetSuite REST / SOAP APIs receive Customer, Sales Order, Invoice, and (optionally) custom Contract records.
Scheduled Reconciliation Jobs run twice daily to catch missed records and flag exceptions.
Centralized Error Queue routes failed jobs to Slack / Teams and email for rapid remediation.
Why Workato? Workato’s connector catalog removes boilerplate API work, but its transactionlevel replay and bulkdata optimization features ensure that highvolume sponsorship seasons do not overwhelm ERP limits.
Design Principles
5. Generalized DataFlow Patterns
Every organization stores sponsorship data a little differently, but the essence of the integration is always the same: move the business context (who, what, when, how much) from the system where it is born into the system that must account for it.
A typical sponsorship deal therefore results in four messages across the bus, each of which is independently recoverable and traceable.
(Detailed object mappings appear in Section 6 and Appendix A.)
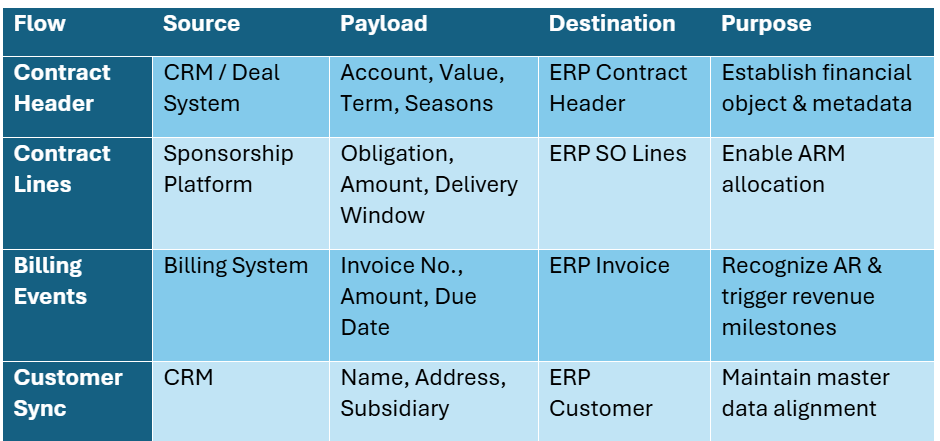
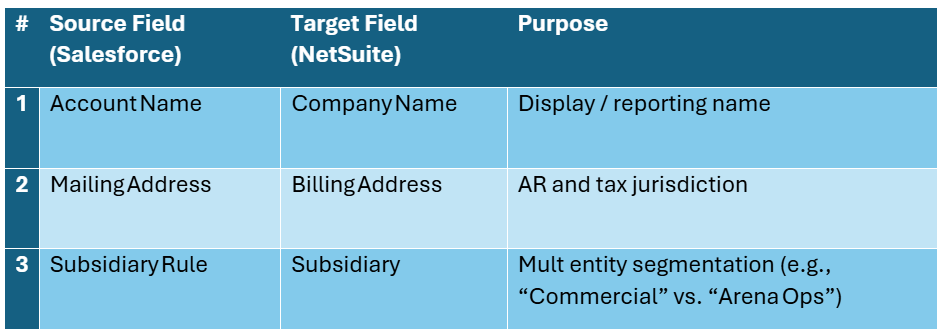
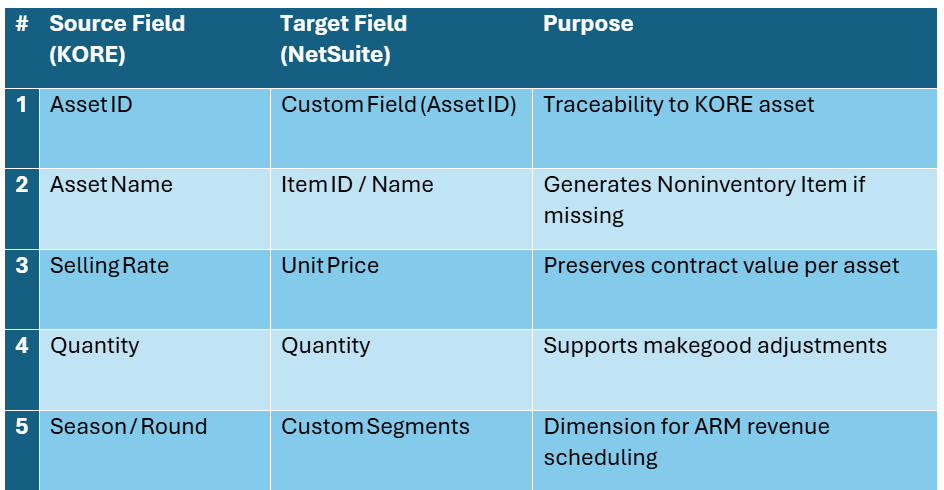
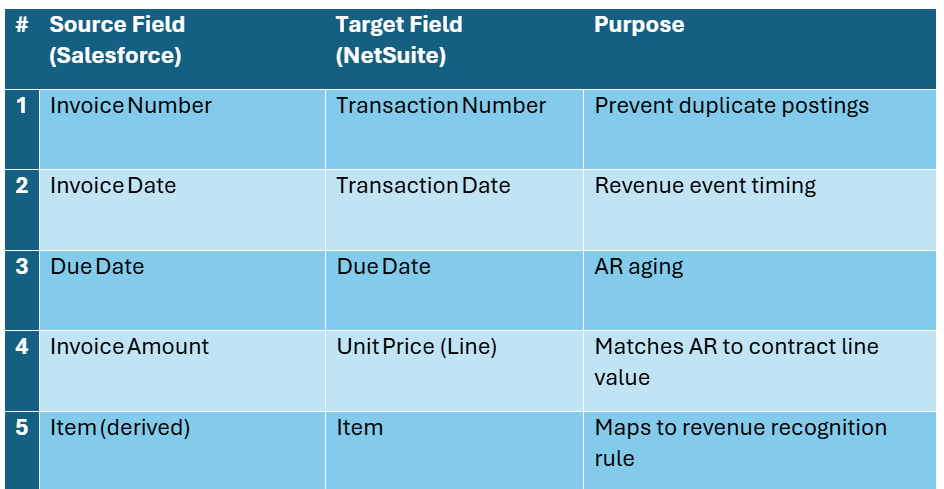
6. Object & Field Mapping (Representative Extract)
The tables below combine frequently referenced attributes for Contract Headers, Customers, Contract Lines/Assets, Invoices, and Metadata. Field labels come directly from our implementation documents but have been generalized so they apply to any professional sports team franchise using the engagement marketing software, Salesforce, and NetSuite. Full, line by line mappings remain proprietary; this extract is sufficient for architects to understand the scope and complexity of the data alignment required.
6.1 Contract (Deal) Header
6.2 Customer (Sponsor)
6.3 Contract Line / Asset
6.4 Invoice Header & Lines
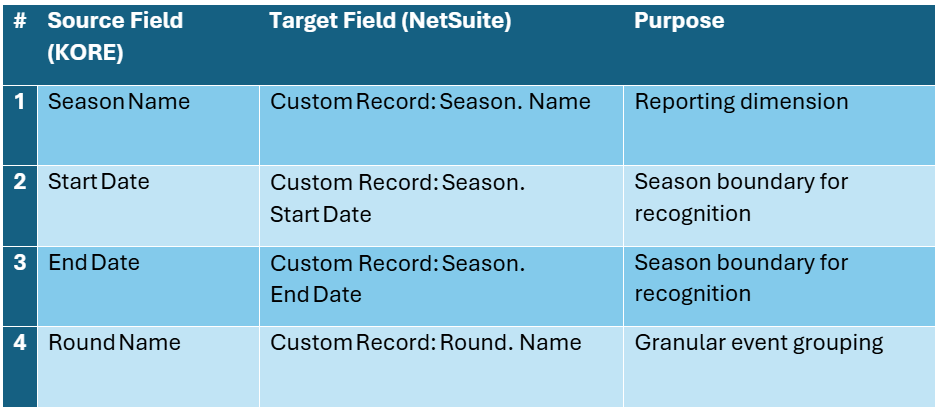
6.5 Metadata (Season & Round)
How to read these tables: “Source Field” refers to the canonical label in engagement marketing software or Salesforce; “Target Field” shows where the data lands in NetSuite. “Purpose” explains why the attribute is critical for automation and compliance.
Part II — NetSuite Advanced Revenue Management (ARM)
(Headings only – functional team to supply details)
7 ARM Implementation Overview
An Advanced Revenue Management and ASC 606 compliance implementation is underway in NetSuite. This project involves integrating data from engagement marketing software, a platform primarily used by Sales teams to manage sponsorship and premium deals, and Salesforce into NetSuite. This document outlines the revenue recognition, billing, and accounting processes that will be handled within NetSuite.
8 Feature Enablement & Dependencies
System Dependencies
Features:
Advanced Revenue Management (Revenue Essentials)
Rule-based Recognition Treatment
Project Management
(NOTE: Per this documentation, Advanced Revenue Management (Revenue Allocation) is not a required feature for the Rule-Based Recognition Treatment: https://docs.oracle.com/en/cloud/saas/netsuite/ns-online-help/chapter_N1675871.html
Accounting Preferences:
Use Sales Price as Fair Value
Consolidate Projects on Sales Transactions
Change Impacts
Use of Sales Orders in NetSuite
New process for in-progress contracts and migrating those over to NetSuite.
Month-end closing process will now shift to automatic Revenue calculations.
Month End Closing tasks in NetSuite:
*Note that the Reclassify Revenue is a native Month End Task that should be skipped for this solution
9 Configuration Building Blocks
Manual Process (via UI, Mass Update and CSV Import)
Configuration of Revenue Rules
Configuration of Item Category
Configuration of Revenue Treatments
Configuration of Revenue Treatment Rules
Configuration of Billing Schedules to be mapped to created Sales Orders
Creation of Setup Intercompany Journal Entry in NS once Deal is Contracted (Automation: Future Phase)
Creation of Adjustment Setup Intercompany Journal Entry in NS every Reallocation of Assets (Automation: Future Phase)
Creation of Customer Payments
Creation of Credit Memo
Creation of Customer Refund
Creation of Customer Payments in SF
Creation of Credit Memo in SF
Creation of Customer Refund in SF
Creation of Events for Calendar Method (via Suitelet)
Run Revenue Recognition Process
Run Revenue Reclassification process
Marking Revenue Plans to UnHold for Revenue Recognition for Items that are dependent on Delivery Matrix from engagement marketing software (Automation: Future Phase)
Native Automation from NetSuite
Mapping of Revenue Rules to Sales Order Line Items
Creation of Revenue Arrangement per Sales Orders/Credit Memos
Creation of Revenue Plans
Update Revenue Arrangements and Revenue Plans
Creation of Revenue Recognition Journal Entries
Creation of Revenue Reclassification Journal Entries
Custom Automations
Creation of Deal Sheet, Deal Sheet Lines, Season Types/Event Types
Groupings and Segregation of Deal Sheet Lines
Creation of Sales Orders
Link SF Invoice to trigger Billing of Invoices to be created in NS
Suitelet for Calendar Events
Creation of Project Records
Creation of Project tasks to be linked to Project.
Linking of Project to Sales Order Lines that are dependent.
Link Credit Memos from NS to SF
Link Payments in NS to SF
Link Customer Refunds in NS to SF
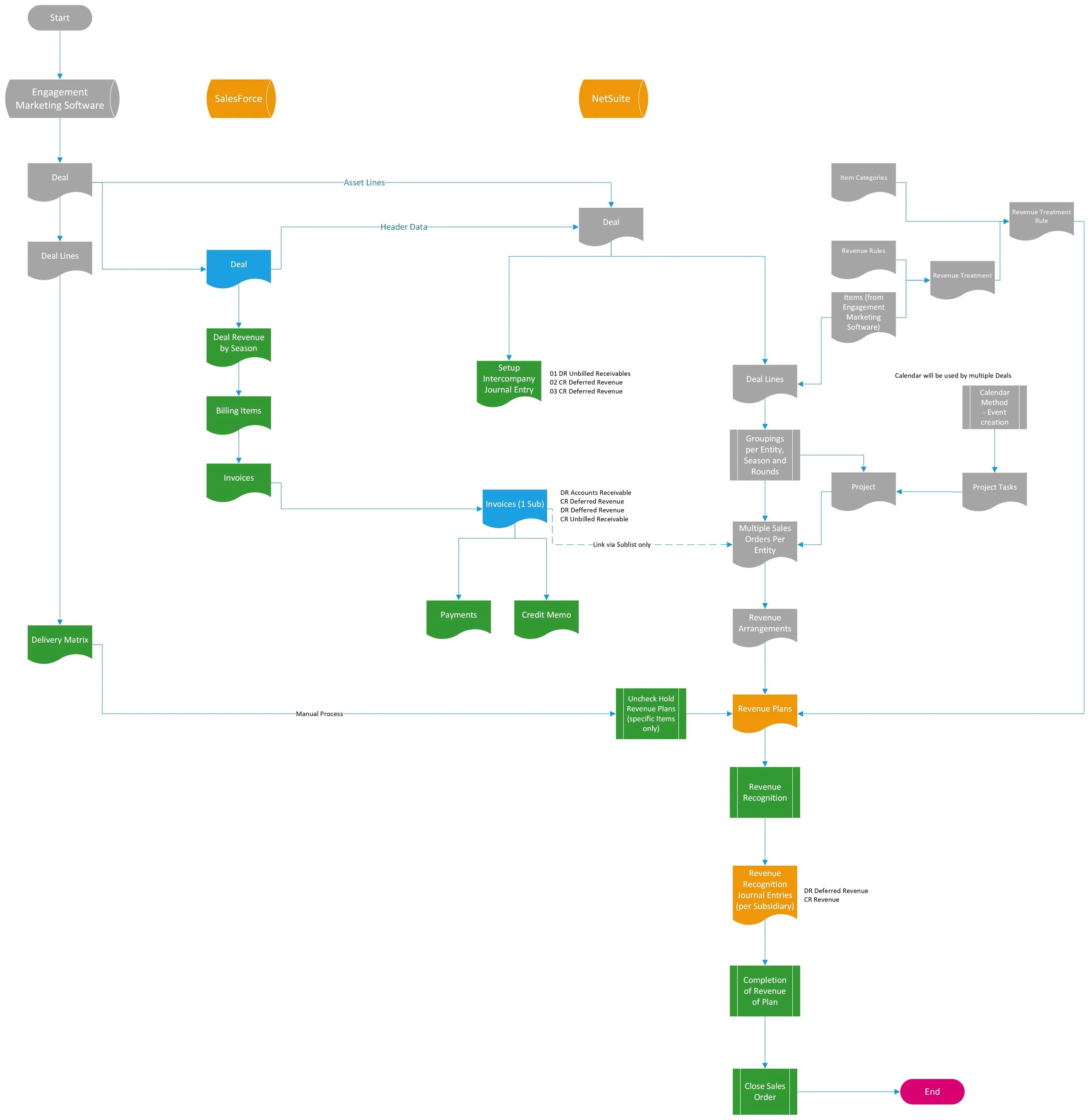
10 Revenue Recognition Process with Month End Close Activities
This workflow outlines the automated process for reallocating and updating revenue data within an integrated system consisting of Engagement Marketing Software and NetSuite. The objective is to ensure that revenue recognition and adjustments (including ASC 606 compliance) are accurately and efficiently reflected, particularly when modifications are made to deal sheet line amounts.
Part III — Delivery & Guidance
13 Error Handling & Monitoring
Seamless integration demands more than simple pointtopoint calls, it requires an ecosystem that detects, analyzes, and resolves issues quickly. Each transaction funnels through Workato’s job framework, which standardizes error responses from engagement marketing software, Salesforce, and NetSuite into a unified format. Should a job fail, the platform retries with exponential backoff, logs contextrich diagnostics, and surfaces realtime alerts to Slack and the ticketing system. A dashboard of key performance indicators, success rate, average latency, and backlog, gives stakeholders an instant health check, while detailed logs make rootcause analysis straightforward.
14 Security & Compliance
Protecting sponsor data and financial records is paramount. The integration follows a defenseindepth model:
Authentication & Authorization. OAuth 2.0 for Salesforce, TokenBased Authentication or REST roles for NetSuite, and API keys or IAM roles for engagement marketing software Redshift ensure each connection is traceable and scoped to minimal permissions.
Data Protection. All traffic travels over TLS, and sensitive credentials are stored in Workato’s encrypted vault. Optional fieldlevel encryption can be applied to payloads at rest.
Auditability. NetSuite’s native audit trail pairs with Workato’s immutable job history to provide evidence suitable for SOX and external audits. Every API call carries a correlation ID, making it simple to tie transactions back to the originating contract.
15 Mini WalkThrough Scenario
Below is a condensed, fictional journey of a single sponsorship contract to illustrate how the pieces come together in practice.
Scenario: A threeseason, $1.2 million digital sponsorship sold to “Acme Corp.”
Day 0 – Deal Closed
Sales rep marks the Opportunity “Closed Won” in Salesforce at 10:15 AM.
• Workato trigger fires <200 ms later.
• Contract header is created in NetSuite with status “Pending Lines.”Day 0 – LineItem Enrichment
Workato calls Engagement Marketing Software’s Sponsorship API to pull eight digital asset lines.
• Lines total $1.2 M, spread evenly across three seasons.
• NetSuite sales order and revenue elements are created; ARM allocates $400 k per season.Day 30 – First Invoice Issued
Finance generates a 30% upfront invoice in Salesforce.
• Invoice syncs to NetSuite within 60 s.
• ARM applies the payment to the first season’s revenue plan; revenue schedule autoposts monthly JEs.Day 45 – Error & Recovery
A new asset line is added in Engagement Marketing Software but maps to an unknown Item ID in NetSuite.
• Workato recipe fails validation, routes to Exceptions queue.
• Notification appears in Slack; finance adds the missing Item record.
• Admin replays the failed job; line imports successfully, maintaining audit continuity.Season Close – Automated Recognition
At season end, ARM marks $400k recognized, $800k deferred.
• NetSuite dashboards show realtime recognized vs. deferred revenue.
• Sales leadership views the same figures via embedded NetSuite reports in Salesforce.
Outcome: Contract is fully synchronized across systems with less than five minutes of manual intervention, only to resolve the new Item mapping.
16 Implementation Considerations
Before launching an integration of this scope, organizations should assess readiness across three areas:
Typical Timeline Range: 12–18 weeks for a midsized professional sports team franchise, including discovery, build, UAT, and cutover, assuming dedicated resources and no major legacy data cleanup. Teams with complex historical contracts or multiple billing systems may extend the timeline.
Tip: Engaging an implementation partner with prior Engagement Marketing Software SalesforceNetSuite experience can cut discovery time by up to 30% and surface edge cases early, reducing overall risk.
17 Conclusion & Next Steps
An integrated Engagement Marketing Software SalesforceNetSuite stack turns sponsorship contracts into streamlined, compliant revenue streams. Organizations ready to move beyond spreadsheets should validate data quality, enable ARM in a sandbox, and pilot a single contract through the full lifecycle. Selecting an iPaaS with robust monitoring, as detailed here, lays the groundwork for scalable automation. Finally, consider engaging experts who have navigated these platforms in sportsrevenue scenarios to accelerate delivery and minimize surprises.
© 2025 , For illustrative purposes only. All product names are trademarks of their respective owners.